 Editor’s note: This commentary from Jude Schwallbach, research associate and project coordinator at The Heritage Foundation, originally appeared in The Daily Signal.
Editor’s note: This commentary from Jude Schwallbach, research associate and project coordinator at The Heritage Foundation, originally appeared in The Daily Signal.
 National School Choice Week has taken on renewed importance this year, as too many families are approaching the one-year mark of crisis online learning provided by their public school district.
National School Choice Week has taken on renewed importance this year, as too many families are approaching the one-year mark of crisis online learning provided by their public school district.
Last March, the coronavirus pandemic shuttered schools nationwide, forcing teachers, parents, and students to transition to virtual classrooms and grapple with the various effects of lockdowns. Ten months later, parents report that 53% of K-12 students are still learning in their virtual classrooms.
Public schools have remained largely closed to in-person instruction.
Recent research by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicated that in-person learning is rarely a source of large outbreak. Even though in-person learning is one of the safest activities for children, proposals to reopen district schools for face-to-face learning have met with staunch opposition from teachers’ unions.
Inexplicably, teachers unions have also rejected measures which would require teachers to be more available to students throughout the day via live video.
The Center on Reinventing Public Education’s director, Robin Lake, told the New York Times that the teachers unions’ vacillating responses feel “like we are treating kids as pawns in this game.”
Adding to parents’ frustrations, teachers unions have also taken the opportunity to push for a whole host of concessions that have nothing to do with health safety.
For instance, the American Federation of Teachers has a long list of demands, including: additional food programs, guidance counselors, smaller classes, tutors to assist teachers, and “culturally responsive practices.”
Similarly, The United Teachers of Los Angeles has demanded a moratorium on charter schools, higher taxes for the wealthy, and “Medicare for All.”
The blatant, non-pandemic-related demands of many teachers unions have illustrated what Stanford University professor Terry Moe noted a decade ago: “This is a school system organized for the benefit of the people who work in it, not for the kids they are expected to teach.”
The inflexibility of teachers unions has increasingly become a source of escalating tension with local officials. For example, Chicago Public Schools, the third largest school district in the nation, locked teachers out of their virtual classrooms after they refused to return to in-person instruction with classrooms at less than 20% capacity.
Such unbending posture has provoked the ire of parents and left many children frustrated, both academically and socially. As Tim Carne wrote in the Washington Examiner, “The very people who have most loudly declared the importance of public schools now are deliberately destroying public schools.”
Many parents are tired of being strong-armed by teachers unions and have pursued alternative education options for their children.
For instance, the learning pod phenomenon, wherein parents work together to pool resources and hire their own tutors and materials is popular. This allows students to return to in-person lessons, even if school districts refuse to reopen.
Last September, a national poll by the pro-school choice nonprofit EdChoice indicated that 18% of surveyed parents were looking to join one. At the same time, 70% of surveyed teachers reported interest in teaching in a pod.
A recent report by education scholars Michael B. Henderson, Paul Peterson, and Martin West found that approximately 3 million students—nearly 6% of K-12 students—currently participate in a learning pod.
Notably, pod participants are more likely to be “from families in the bottom quartile of the income distribution.” The authors wrote, “Parent reports suggest that 9% of all students from low-income families and 5% of all students from high-income families are participating in pods.”
Families have embraced private school options, too. A survey last November of 160 schools in 15 states and Washington, D.C., showed that half of the surveyed private schools experienced higher enrollment this academic year than they had the previous year pre-pandemic.
Moreover, more than 75% of surveyed private schools were open for in-person instruction. The remaining schools offered hybrid education, which is a combination of in-person and virtual learning.
Children could have greater access to private education if more states made education dollars student-centered. For instance, parent controlled education savings accounts allow parents to spend their funds on approved education costs, like private tutoring, books, or tuition. These accounts already exist in five states.
National School Choice Week is an important reminder that “public education” means education available to the public, regardless of the type of school it takes place in. It is the perfect time to remember that parents, not teachers unions, are best positioned to determine the education needs of children.
School choice options like education savings accounts can bring education consistency to families across the country during a most uncertain time. National School Choice Week is an important reminder of that.
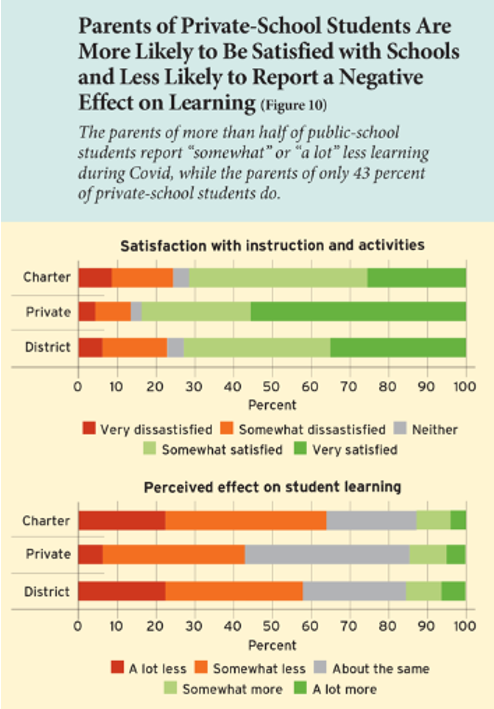
 Nearly a year after the COVID-19 pandemic began and reshaped the nation’s education system, parents of private and charter school students are more likely to be satisfied with their schools and less likely to report a negative effect on learning than their public school counterparts. That’s a key finding in the latest survey from Education Next.
Nearly a year after the COVID-19 pandemic began and reshaped the nation’s education system, parents of private and charter school students are more likely to be satisfied with their schools and less likely to report a negative effect on learning than their public school counterparts. That’s a key finding in the latest survey from Education Next.
The survey was conducted by Michael B. Henderson of the University of Louisiana, and Martin West and Paul E. Peterson, both of Harvard University. The researchers surveyed 2,155 American parents with children in grades K-12 in December, examining parental satisfaction as well as the impacts of remote and hybrid learning on students since the pandemic started.
As with the last survey in September, parents expressed general satisfaction even as their children are learning less. Private school students continue to be more likely to receive in-person instruction, where parents are more likely to report lower levels of learning loss and lower negative impacts on the student’s social, emotional and physical well-being. Overall, parents are generally satisfied with schools (71% district, 73% charter and 83% private). Private school parents are more likely to be very satisfied – 55% – compared to 35% for charter parents and 25% of district parents.
Just 18% of private school parents reported their children were learning remotely, compared to more than half for district and charter school students.
Despite this broad satisfaction across sectors, 60% believe their children are learning less than they did before. In-person learning was closely related to higher reported satisfaction and lower reported learning losses.
A small difference exists between sectors regarding impacts on “student’s academic knowledge,” with 38% of district parents reporting negative impacts to 30% of private school parents. A similar 8-point difference was observed for parents reporting negative effects on their child’s emotional well-being.
Parents do report significantly higher negative impacts on their child’s social relationships and physical fitness at district and charter schools compared to private ones.
Private schools offering remote learning do lag behind their counterparts for teachers meeting with the entire class, but there’s little difference on one-on-one teacher student meetings. Remote private schools also lag behind on weekly homework assignments (84% of parents report weekly assignments) compared to district schools (93% of parents report weekly assignments).
The survey also makes several interesting observations.
While district enrollment fell 9 percentage points between the Spring and Fall of 2020, researchers found it had little to do with the school districts’ response to the Covid pandemic.
Just 10% of new private school students and 14% of new charter school students switched due to dissatisfaction with their prior school’s response to Covid. However, among new home school parents, 61% were dissatisfied with their prior school’s response to Covid.
Meanwhile, 32% of private school parents and 19% of charter parents were dissatisfied with their prior school in some way. Parents were more likely to switch schools because of moving or because their prior school no longer offered the child’s grade level.
Covid safety appears to be roughly similar across sectors. While private school students are far more likely to attend school in person, parents across all sectors report incidents of Covid infections at roughly the same rate. Parents also equally report their school sector is doing “about the right amount,” when it comes to Covid safety measures.
Another discovery was the rate at which parents utilized in-person learning when compared to local Covid infection rates. Counties in highest quartile of infection rates offered more in-person learning options than counties with the lowest options.
Despite noting this “perverse result,” researchers also state that the observed result does “not constitute evidence that greater use of in-person learning contributed to the spread of the virus across the United States.”
Despite children learning less, parents are generally satisfied across all school sectors.
 This commentary from redefinED guest blogger Jonathan Butcher, senior policy analyst at the Heritage Foundation’s Center for Education Policy, and center director Lindsey Burke, first appeared on Tribune News Service.
This commentary from redefinED guest blogger Jonathan Butcher, senior policy analyst at the Heritage Foundation’s Center for Education Policy, and center director Lindsey Burke, first appeared on Tribune News Service.
When it comes to her daughter Emerson’s education, Sarrin Warfield says, she’s “in it to win it.”
When Emerson’s assigned school in South Carolina announced plans for virtual learning this fall, Sarrin says she asked herself, “What if we just made this in my backyard and made a school?” After talking with friends who have children the same age as Emerson, Sarrin said, “Let’s do it. Instead of it being a crazy idea, let’s own this process and be really intentional about doing this and make it happen.”
Sarrin is one of the thousands of parents around the country who formed learning pods when assigned schools closed. By meeting in small groups with friends’ and neighbors’ children, these pod families could try to keep at least one of part of their child’s life from being upended because of COVID-19.
The time-honored practice of school assignment did little to help the Warfields — or thousands of other students around the U.S. during the COVID spring … and then COVID summer and fall. In the beginning of the 2020-2021 school year, officials in some of the largest districts in the country reported significant enrollment changes from the previous school year, especially among younger students.
Officials in Mesa, Arizona, reported a 17% decrease in kindergarten enrollment after the first two weeks. In Los Angeles, Superintendent Austin Beutner reported a 3.4% decrease in enrollment, but said another 4% of students couldn’t be found, making the change closer to 7%. Figures are similar in Broward County, Florida, and Houston. In large school districts, these percentages amount to over 10,000 children per district.
Some of these changes can be attributed to learning pods. But officials in large cities and even those representing entire states simply reported having no contact with many students.
Under normal circumstances, if thousands of children who were once in school suddenly were nowhere to be found, this would be an issue of national concern. Hearings would be held, and officials would demand to know what is happening with schools around the country. Loud calls for change would be heard.
But life during the pandemic is anything but normal.
Likewise, if more students around the country were failing — say, twice the figure from last year — this would also be worrisome, right? From Los Angeles to Houston to Chicago to Fairfax, Virginia, school officials and researchers are now reporting that the proportion of students earning D’s and F’s in the first semester has increased, doubling in some cases, in comparison to the last school year.
Yet across the U.S., many school districts, especially those in large metro areas, remain closed to in-person learning for some if not all grades and may not reopen at the start of 2021.
According to the Pew Research Center, 72% of parents in lower-income brackets report being “very” or “somewhat” concerned this fall that their children are “falling behind in school as a result of the disruptions caused by the pandemic.” With thousands of students not in class, even virtually, and falling grades among those who are attending, who can blame them?
For taxpayers and policymakers looking for lessons in the pandemic, the utter failure of school assignment systems to provide quality-learning options to all students, especially the most vulnerable, is clear.
The quality and consistency of the education a child received during the pandemic has been dependent on the attendance boundary in which that child’s family lives. At the same time, so many of the issues plaguing education during the pandemic — and for that matter, the entire century leading up to the pandemic — are rooted in policies that fund school systems, rather than individual students.
Allowing dollars to follow children directly to any public or private school of choice is a critical emergency policy reform that states should pursue. Such a policy change is overdue.
Since it’s anyone’s guess how soon life will get back to normal, we can’t wait any longer for the system to fix itself.